A Dive to the Build Process
What Goes On When You Press the Play Button
Previously
A Build is the process of transforming code to an executable

Today
We dive a bit deeper but not too deep
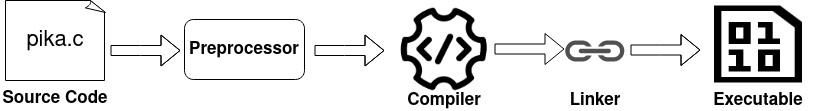
GCC Build Process
Your compiler does more than compiling code
Preprocessor
Expands Source Code
Gives ability to:
Preprocessor - MACRO
- substitute text -
RECALL: In C89, there is no variable length array support
int max_buffer_size = 10;
int arr[max_buffer_size];
THIS IS ILLEGAL
Solution
- Use a MACRO -
# define MAX_BUFFER_SIZE 10
int main() {
int arr[MAX_BUFFER_SIZE];
// Rest of the code
int main() {
int arr[10];
//Rest of the code
Preprocessor Madness
#include "include.h"
#include "declare_main.h"
#include "open_bracket.h"
#include "print_hello.h"
#include "close_bracket.h"
Each "header" file contains a line of C code
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
printf("Hello World\n");
}Conditional Macros
- You can choose which source code will be compiled -
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("File: %s on line %d", __FILE, __LINE);
printf("Value of x: %d\n", x);
#endif
-DDEBUG, the print statements will be
generated in the file the compiler processes

Include Directive
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}
After preprocessing, the code becomes 720 lines from 5 lines!!!75B Source Code to 15.6KB
# 1 "main.c"
# 1 ""
# 1 ""
# 31 ""
# 1 "/usr/include/stdc-predef.h" 1 3 4
# 32 "" 2
# 1 "main.c"
# 1 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 1 3 4
# 27 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/libc-header-start.h" 1 3 4
# 33 "/usr/include/bits/libc-header-start.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/features.h" 1 3 4
# 428 "/usr/include/features.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 1 3 4
# 442 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4
# 443 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/long-double.h" 1 3 4
# 444 "/usr/include/sys/cdefs.h" 2 3 4
# 429 "/usr/include/features.h" 2 3 4
# 452 "/usr/include/features.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 1 3 4
# 10 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs-64.h" 1 3 4
# 11 "/usr/include/gnu/stubs.h" 2 3 4
# 453 "/usr/include/features.h" 2 3 4
# 34 "/usr/include/bits/libc-header-start.h" 2 3 4
# 28 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8/include/stddef.h" 1 3 4
# 216 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8/include/stddef.h" 3 4
# 216 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8/include/stddef.h" 3 4
typedef long unsigned int size_t;
# 34 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8/include/stdarg.h" 1 3 4
# 40 "/usr/lib/gcc/x86_64-redhat-linux/8/include/stdarg.h" 3 4
typedef __builtin_va_list __gnuc_va_list;
# 37 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 1 3 4
# 27 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/wordsize.h" 1 3 4
# 28 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 2 3 4
typedef unsigned char __u_char;
typedef unsigned short int __u_short;
typedef unsigned int __u_int;
typedef unsigned long int __u_long;
typedef signed char __int8_t;
typedef unsigned char __uint8_t;
typedef signed short int __int16_t;
typedef unsigned short int __uint16_t;
typedef signed int __int32_t;
typedef unsigned int __uint32_t;
typedef signed long int __int64_t;
typedef unsigned long int __uint64_t;
typedef __int8_t __int_least8_t;
typedef __uint8_t __uint_least8_t;
typedef __int16_t __int_least16_t;
typedef __uint16_t __uint_least16_t;
typedef __int32_t __int_least32_t;
typedef __uint32_t __uint_least32_t;
typedef __int64_t __int_least64_t;
typedef __uint64_t __uint_least64_t;
typedef long int __quad_t;
typedef unsigned long int __u_quad_t;
typedef long int __intmax_t;
typedef unsigned long int __uintmax_t;
# 140 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/typesizes.h" 1 3 4
# 141 "/usr/include/bits/types.h" 2 3 4
typedef unsigned long int __dev_t;
typedef unsigned int __uid_t;
typedef unsigned int __gid_t;
typedef unsigned long int __ino_t;
typedef unsigned long int __ino64_t;
typedef unsigned int __mode_t;
typedef unsigned long int __nlink_t;
typedef long int __off_t;
typedef long int __off64_t;
typedef int __pid_t;
typedef struct { int __val[2]; } __fsid_t;
typedef long int __clock_t;
typedef unsigned long int __rlim_t;
typedef unsigned long int __rlim64_t;
typedef unsigned int __id_t;
typedef long int __time_t;
typedef unsigned int __useconds_t;
typedef long int __suseconds_t;
typedef int __daddr_t;
typedef int __key_t;
typedef int __clockid_t;
typedef void * __timer_t;
typedef long int __blksize_t;
typedef long int __blkcnt_t;
typedef long int __blkcnt64_t;
typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt_t;
typedef unsigned long int __fsblkcnt64_t;
typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt_t;
typedef unsigned long int __fsfilcnt64_t;
typedef long int __fsword_t;
typedef long int __ssize_t;
typedef long int __syscall_slong_t;
typedef unsigned long int __syscall_ulong_t;
typedef __off64_t __loff_t;
typedef char *__caddr_t;
typedef long int __intptr_t;
typedef unsigned int __socklen_t;
typedef int __sig_atomic_t;
# 39 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/types/__fpos_t.h" 1 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/types/__mbstate_t.h" 1 3 4
# 13 "/usr/include/bits/types/__mbstate_t.h" 3 4
typedef struct
{
int __count;
union
{
unsigned int __wch;
char __wchb[4];
} __value;
} __mbstate_t;
# 6 "/usr/include/bits/types/__fpos_t.h" 2 3 4
typedef struct _G_fpos_t
{
__off_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} __fpos_t;
# 40 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/types/__fpos64_t.h" 1 3 4
# 10 "/usr/include/bits/types/__fpos64_t.h" 3 4
typedef struct _G_fpos64_t
{
__off64_t __pos;
__mbstate_t __state;
} __fpos64_t;
# 41 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/types/__FILE.h" 1 3 4
struct _IO_FILE;
typedef struct _IO_FILE __FILE;
# 42 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/types/FILE.h" 1 3 4
struct _IO_FILE;
typedef struct _IO_FILE FILE;
# 43 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/types/struct_FILE.h" 1 3 4
# 35 "/usr/include/bits/types/struct_FILE.h" 3 4
struct _IO_FILE;
struct _IO_marker;
struct _IO_codecvt;
struct _IO_wide_data;
typedef void _IO_lock_t;
struct _IO_FILE
{
int _flags;
char *_IO_read_ptr;
char *_IO_read_end;
char *_IO_read_base;
char *_IO_write_base;
char *_IO_write_ptr;
char *_IO_write_end;
char *_IO_buf_base;
char *_IO_buf_end;
char *_IO_save_base;
char *_IO_backup_base;
char *_IO_save_end;
struct _IO_marker *_markers;
struct _IO_FILE *_chain;
int _fileno;
int _flags2;
__off_t _old_offset;
unsigned short _cur_column;
signed char _vtable_offset;
char _shortbuf[1];
_IO_lock_t *_lock;
__off64_t _offset;
struct _IO_codecvt *_codecvt;
struct _IO_wide_data *_wide_data;
struct _IO_FILE *_freeres_list;
void *_freeres_buf;
size_t __pad5;
int _mode;
char _unused2[15 * sizeof (int) - 4 * sizeof (void *) - sizeof (size_t)];
};
# 44 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
# 52 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef __gnuc_va_list va_list;
# 63 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef __off_t off_t;
# 77 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
typedef __ssize_t ssize_t;
typedef __fpos_t fpos_t;
# 133 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/stdio_lim.h" 1 3 4
# 134 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
extern FILE *stdin;
extern FILE *stdout;
extern FILE *stderr;
extern int remove (const char *__filename) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int rename (const char *__old, const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int renameat (int __oldfd, const char *__old, int __newfd,
const char *__new) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 173 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *tmpfile (void) ;
# 187 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern char *tmpnam (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern char *tmpnam_r (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# 204 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern char *tempnam (const char *__dir, const char *__pfx)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__malloc__)) ;
extern int fclose (FILE *__stream);
extern int fflush (FILE *__stream);
# 227 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fflush_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
# 246 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes) ;
extern FILE *freopen (const char *__restrict __filename,
const char *__restrict __modes,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
# 279 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fdopen (int __fd, const char *__modes) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# 292 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *fmemopen (void *__s, size_t __len, const char *__modes)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern FILE *open_memstream (char **__bufloc, size_t *__sizeloc) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern void setbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int setvbuf (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
int __modes, size_t __n) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern void setbuffer (FILE *__restrict __stream, char *__restrict __buf,
size_t __size) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern void setlinebuf (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int fprintf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...);
extern int printf (const char *__restrict __format, ...);
extern int sprintf (char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int vfprintf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg);
extern int vprintf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg);
extern int vsprintf (char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__));
extern int snprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, ...)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 3, 4)));
extern int vsnprintf (char *__restrict __s, size_t __maxlen,
const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 3, 0)));
# 379 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vdprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 2, 0)));
extern int dprintf (int __fd, const char *__restrict __fmt, ...)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__printf__, 2, 3)));
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) ;
extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) ;
extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, ...) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 409 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fscanf (FILE *__restrict __stream, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_fscanf")
;
extern int scanf (const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_scanf")
;
extern int sscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, ...) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_sscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__))
;
# 434 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format,
__gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))) ;
extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 1, 0))) ;
extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s,
const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg)
__attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) __attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0)));
# 457 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int vfscanf (FILE *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vfscanf")
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0))) ;
extern int vscanf (const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vscanf")
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 1, 0))) ;
extern int vsscanf (const char *__restrict __s, const char *__restrict __format, __gnuc_va_list __arg) __asm__ ("" "__isoc99_vsscanf") __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__))
__attribute__ ((__format__ (__scanf__, 2, 0)));
# 491 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getc (FILE *__stream);
extern int getchar (void);
extern int getc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
extern int getchar_unlocked (void);
# 516 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetc_unlocked (FILE *__stream);
# 527 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fputc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putchar (int __c);
# 543 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fputc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putc_unlocked (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern int putchar_unlocked (int __c);
extern int getw (FILE *__stream);
extern int putw (int __w, FILE *__stream);
extern char *fgets (char *__restrict __s, int __n, FILE *__restrict __stream)
;
# 609 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern __ssize_t __getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern __ssize_t getdelim (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n, int __delimiter,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern __ssize_t getline (char **__restrict __lineptr,
size_t *__restrict __n,
FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern int fputs (const char *__restrict __s, FILE *__restrict __stream);
extern int puts (const char *__s);
extern int ungetc (int __c, FILE *__stream);
extern size_t fread (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern size_t fwrite (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __s);
# 679 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern size_t fread_unlocked (void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream) ;
extern size_t fwrite_unlocked (const void *__restrict __ptr, size_t __size,
size_t __n, FILE *__restrict __stream);
extern int fseek (FILE *__stream, long int __off, int __whence);
extern long int ftell (FILE *__stream) ;
extern void rewind (FILE *__stream);
# 713 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fseeko (FILE *__stream, __off_t __off, int __whence);
extern __off_t ftello (FILE *__stream) ;
# 737 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int fgetpos (FILE *__restrict __stream, fpos_t *__restrict __pos);
extern int fsetpos (FILE *__stream, const fpos_t *__pos);
# 763 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern void clearerr (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int feof (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern int ferror (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern void clearerr_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int feof_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern int ferror_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern void perror (const char *__s);
# 1 "/usr/include/bits/sys_errlist.h" 1 3 4
# 26 "/usr/include/bits/sys_errlist.h" 3 4
extern int sys_nerr;
extern const char *const sys_errlist[];
# 788 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 2 3 4
extern int fileno (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern int fileno_unlocked (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
# 806 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern FILE *popen (const char *__command, const char *__modes) ;
extern int pclose (FILE *__stream);
extern char *ctermid (char *__s) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 846 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern void flockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
extern int ftrylockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__)) ;
extern void funlockfile (FILE *__stream) __attribute__ ((__nothrow__ , __leaf__));
# 864 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
extern int __uflow (FILE *);
extern int __overflow (FILE *, int);
# 879 "/usr/include/stdio.h" 3 4
# 2 "main.c" 2
# 3 "main.c"
int main () {
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
} What you are seeing is all the function declarations from stdio.h library
Note: Declaration is telling the compiler the existence of identifiers (i.e. functions) without the complete definition/implementation.Compiler
- Translates C code to Assembly -
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello World\n");
return 0;
}
.file "main.c"
.text
.section .rodata
.LC0:
.string "Hello World"
.text
.globl main
.type main, @function
main:
.LFB0:
.cfi_startproc
pushq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_offset 16
.cfi_offset 6, -16
movq %rsp, %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa_register 6
movl $.LC0, %edi
call puts
movl $0, %eax
popq %rbp
.cfi_def_cfa 7, 8
ret
.cfi_endproc
.LFE0:
.size main, .-main
.ident "GCC: (GNU) 8.3.1 20191121 (Red Hat 8.3.1-5)"
.section .note.GNU-stack,"",@progbits
Assembler
- Converts Assembly to Object Files -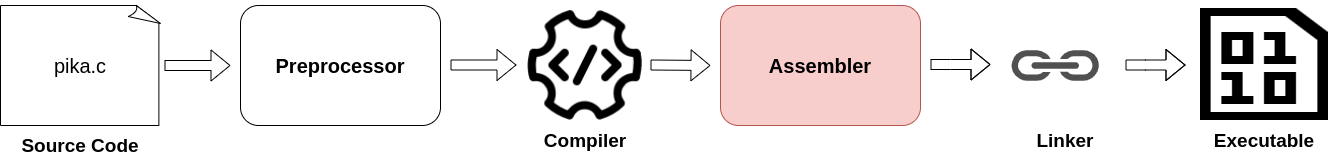
Object Files
- 3 MAIN TYPES: -
- Shared Object File
- Relocatable Object File
- Executable Object File
The file generated from the assembler is a RELOCATABLE OBJECT FILE
Not Executable even though file is in binary
$ gcc -c test.c -o test.o
$ chmod +x test.o
$ ./test.o
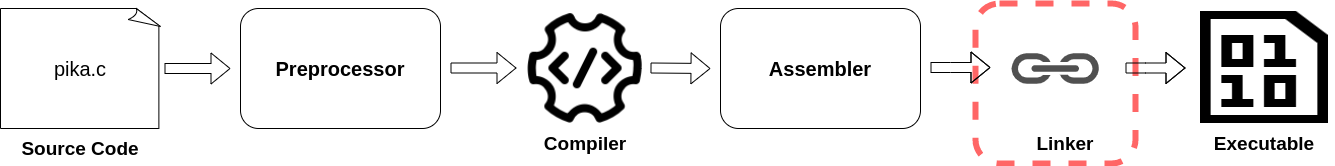
-bash: ./test.o: cannot execute binary file: Exec format error Linker
Combines multiple object files into one executable file

main.c
void honk();
void meow();
int main() {
honk();
meow();
return 0;
} honk and meow are not defined in main.c
How does main.c know about these two functions?
main.c
void honk();
void meow();
int main() {
honk();
meow();
return 0;
} The functions have to be declared to tell the compiler they exist
honk and meow are defined in other source files
#include <stdio.h>
#define PI 3.14
#define Square(x) ((x)*(x))
void honk() {
double area = PI * Square(9); //area = pi * r^2
printf("The Goose Honks the area of the circular pond: %.2f m^2\n", a);
}#include <stdio.h>
void meow() {
printf("The Cat Meows\n");
}Example

void honk();
void meow();
int main() {
honk();
meow();
return 0;
} #include <stdio.h>
#define PI 3.14
#define Square(x) ((x)*(x))
void honk() {
double area = PI * Square(9); //area = pi * r^2
printf("The Goose Honks the area of the circular pond: %.2f m^2\n", a);
}#include <stdio.h>
void meow() {
printf("The Cat Meows\n");
}Preprocessor
gcc -E <file.c>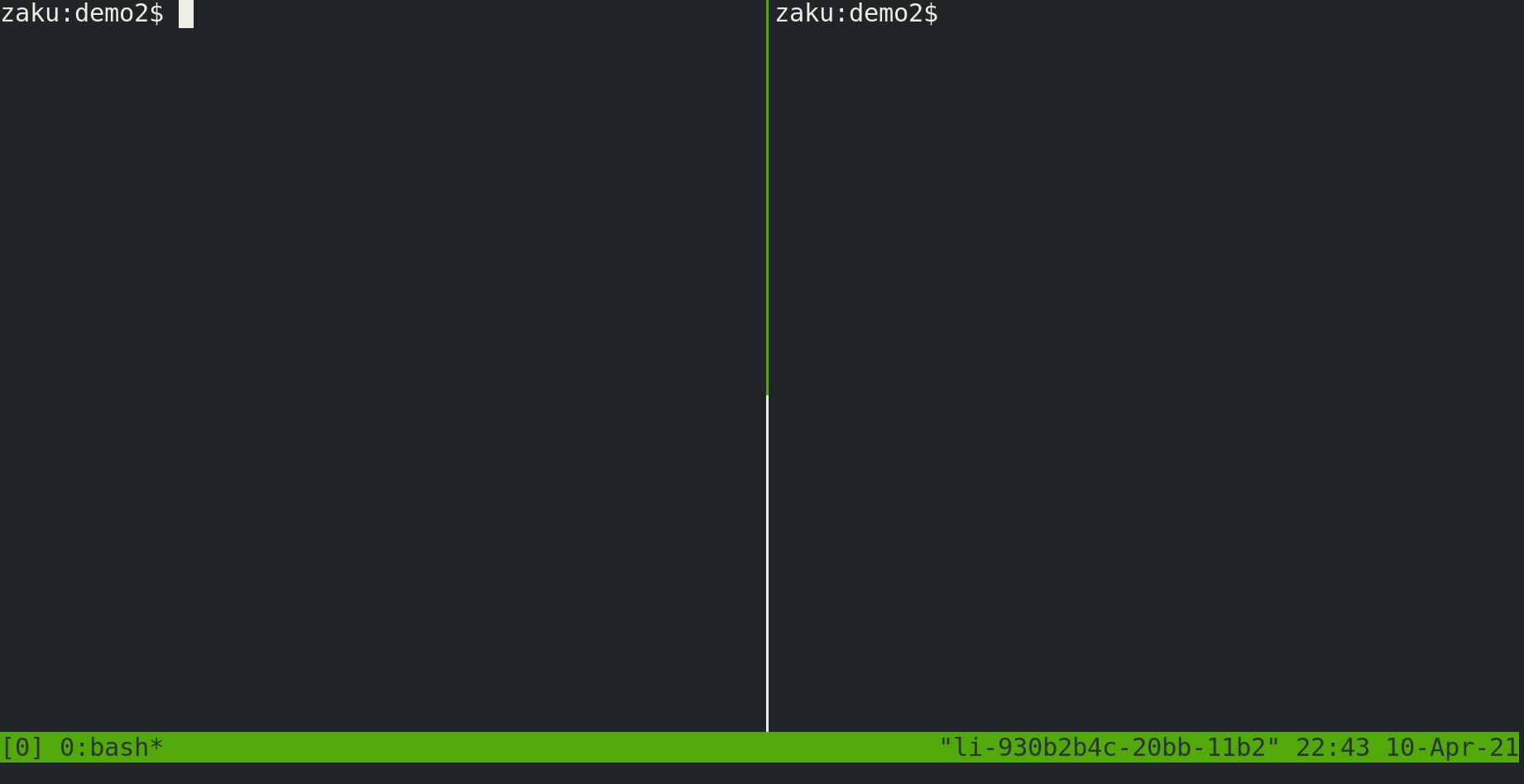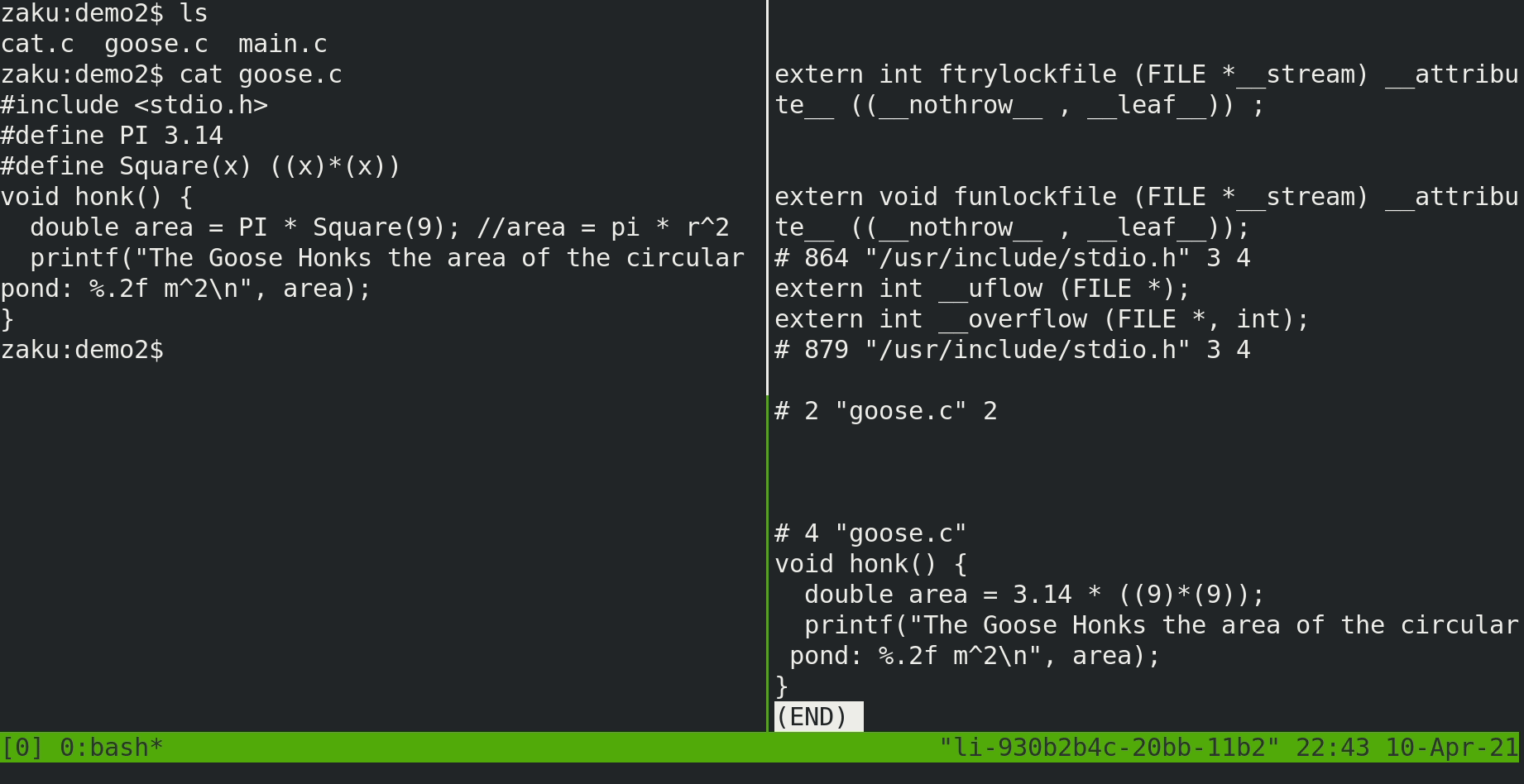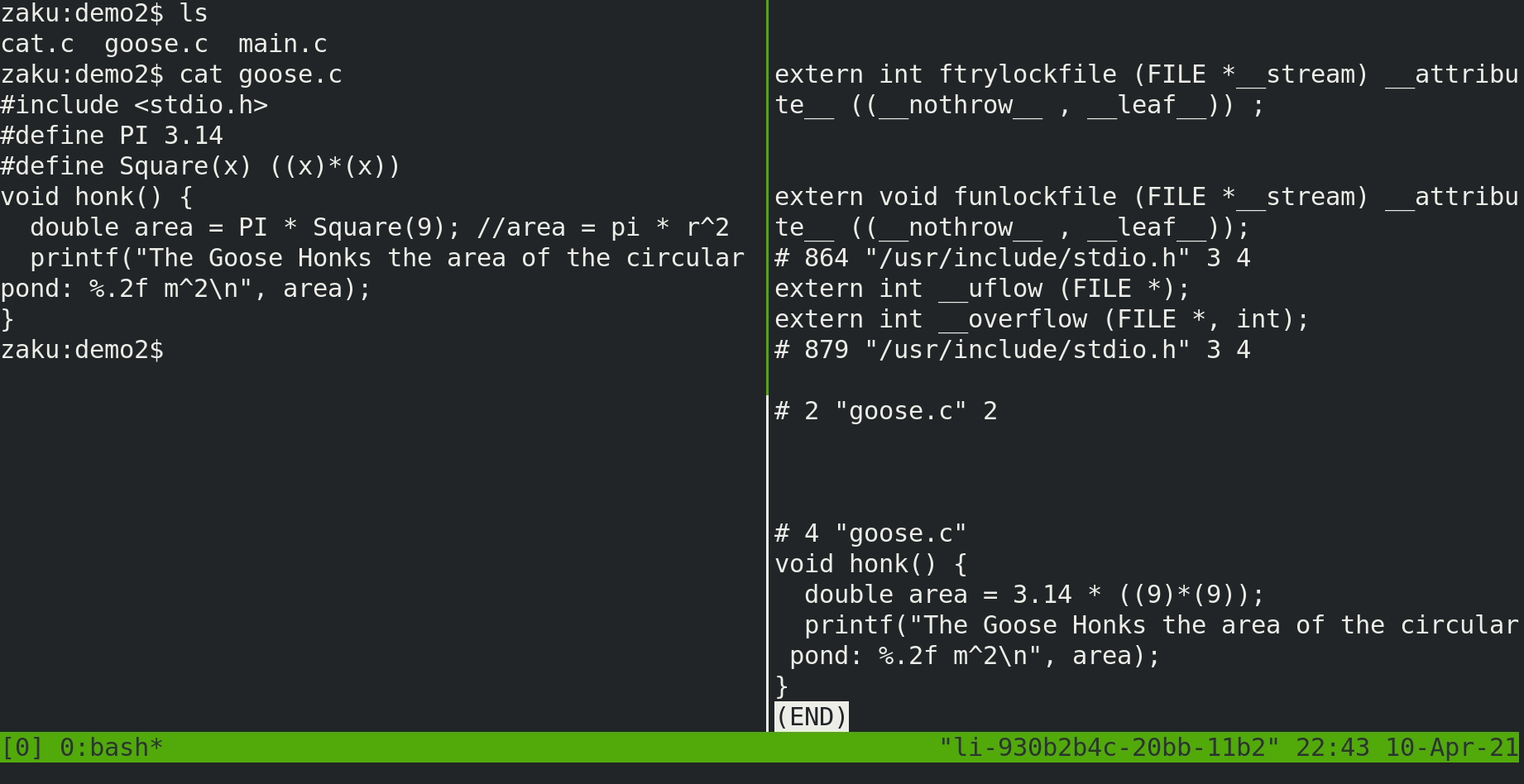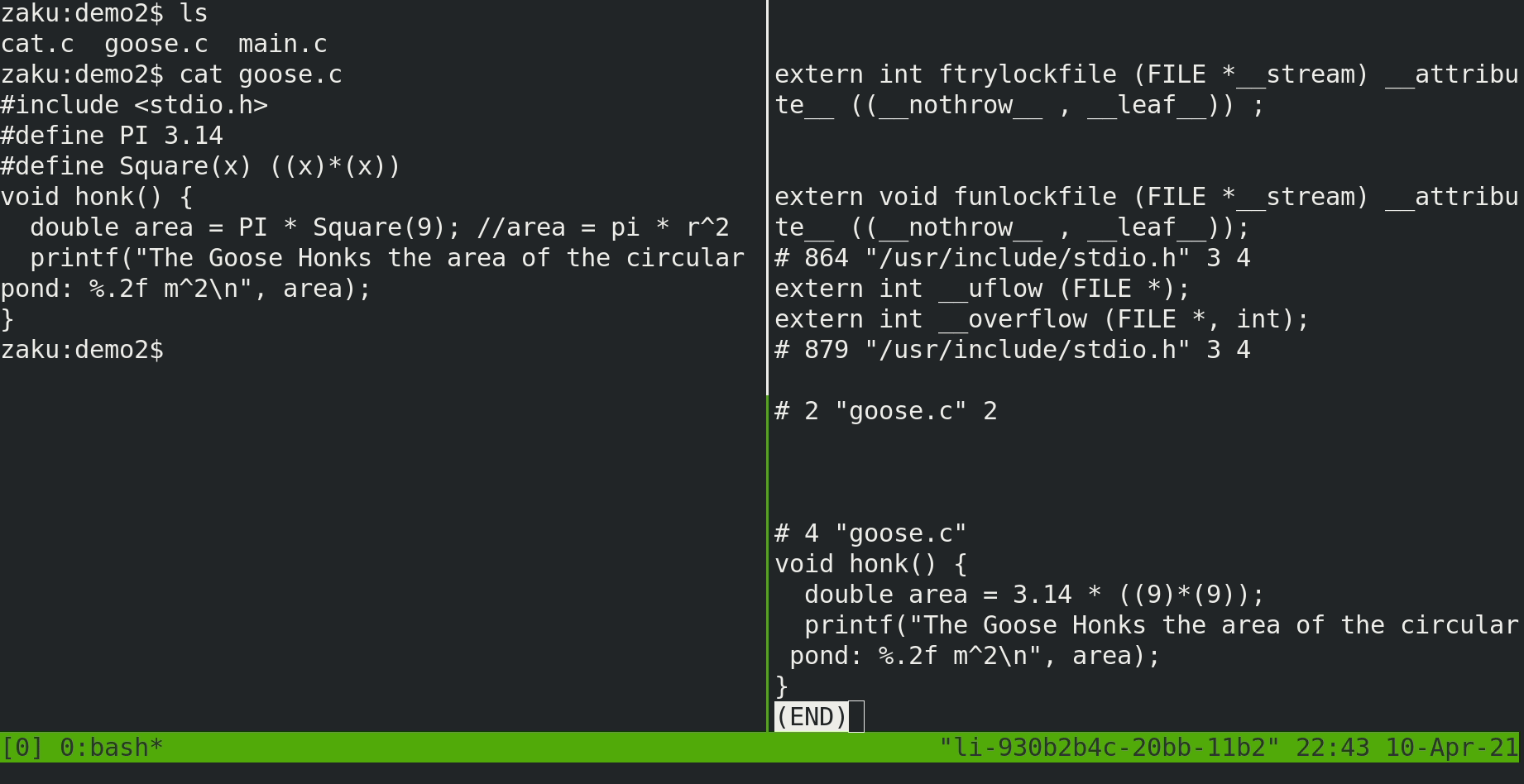
Compilation and Assembler
gcc -c <file.c>Could compile separately gcc -S <file.c> and use as for the assembler as well
$ gcc -c main.c cat.c goose.c
$ ls *.o
cat.o goose.o main.o
gcc -c does preprocessing, compilation, and assembling
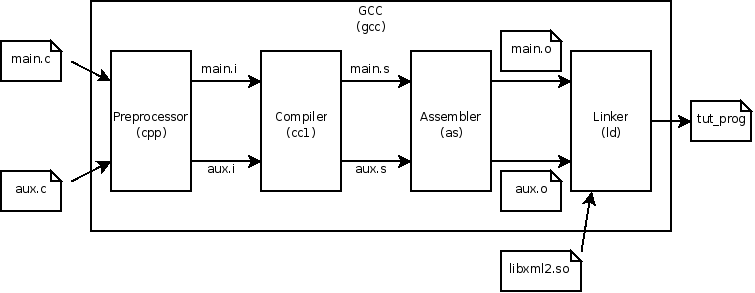
Steps So Far
main.c ⇒ main.i ⇒ main.s ⇒ main.o
$ readelf --syms main.o | grep -E "honk|meow"
9: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT UND honk
10: 0000000000000000 0 NOTYPE GLOBAL DEFAULT UND meowNotice: Object file has absolutely no clue where and what honk & meow are. Hence it appears as UND in the symbol table
Linkers to the rescue
Linkers connect the missing pieces
Simple Idea: ld cat.o goose.o main.o
Actual Command:
ld /usr/lib64/crti.o /usr/lib64/crtn.o /usr/lib64/crt1.o \
>/usr/lib64/libc.so \
>cat.o goose.o main.o
>-dynamic-linker /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 \
>-o progExecute and Run
$ ./prog
The Goose Honks the area of the circular pond: 254.34 m^2
The Cat Meows
$ gcc cat.c goose.c main.c -o progto
$ gcc -E main.c -o main.i
$ gcc -E cat.c -o cat.i
$ gcc -E goose.c -o goose.i
$ gcc -S main.i -o main.s
$ gcc -S cat.i -o cat.s
$ gcc -S goose.i -o goose.s
$ as main.s -o main.o
$ as cat.s -o cat.o
$ as goose.s -o goose.o
$ ld /usr/lib64/crti.o /usr/lib64/crtn.o /usr/lib64/crt1.o \
/usr/lib64/libc.so \
cat.o goose.o main.o \
-dynamic-linker /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 \
-o progQuick Overview of Static Libraries and Dynamic Libraries
In software development, it's very normal for different programs/projects to share the same functions
Example: printf, sqrt, cos, fopen
Libraries allow programmers to reuse common functions among different projects and programs
This saves development time and prevent reventing the wheel
Have a consistent and reliable set of functions with defined behavior
Library Examples
- DirectX SDK (Microsoft's Multimedia API used frequently by Videogame Programmers
- libc (Standard C library)
- asio (C++ Library for network and Low-level I/O programming)
- GTK (GNOME GUI Library) or Qt (another GUI library)
Static Libraries (*.a files)
Static Librares (known as archives are collection of object files
Like archiving files (i.e. zipping files), multiples files become one larger file
 The image is incorrect. It should be archiver and not a linker.
The image is incorrect. It should be archiver and not a linker.
$ ls *.o
cat.o goose.o main.o
$ ar -rs libanimal.a cat.o goose.o
ar: creating animal.a
$ ar -t libanimal.a
cat.o
goose.o$ gcc main.o -L. -lanimal -o prog2
$ ./prog2
The Goose Honks the area of the circular pond: 254.34 m^2
The Cat MeowsBenefits
- If multiple components or projects use the same set of libraries, no need to recompile
- Saves compilation time, compile once and link it each time
Dynamic Libraries (*.so)
Also known as SHARED LIBRARIES
*.dll on WindowsUnlike previous examples where we link object files to create an executable program (BEFORE RUNNING THE PROGRAM),
dynamic libraries are linked during RUNTIME whenever we run the program
As the name implies, dynamic libraries are loaded and linked during RUNTIME
The other name, shared library has a reason, it means multiple programs share the same library in memory by linking to it
How I imagine it
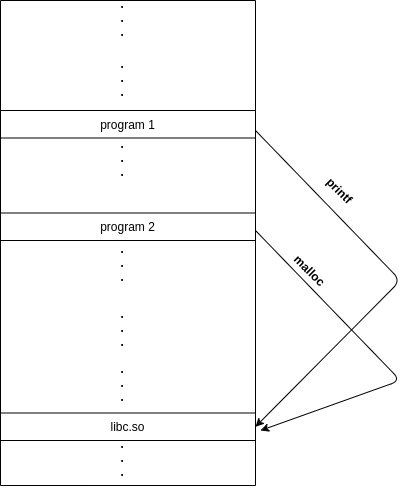
Benefits
- Executable is smaller because definition isn't in the executable itself (i.e. the code for the libraries are stored in the computer at some common location such as /usr/lib
- All programs using the library just need to link to the definition loaded in memory
- Easy to update if a bug exists
LDD - See object Dependencies
$ ldd /bin/ls
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007fff41141000)
libselinux.so.1 => /lib64/libselinux.so.1 (0x00007f11d1688000)
libcap.so.2 => /lib64/libcap.so.2 (0x00007f11d1482000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f11d10bf000)
libpcre2-8.so.0 => /lib64/libpcre2-8.so.0 (0x00007f11d0e3b000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00007f11d0c37000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f11d1ad5000)
libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x00007f11d0a17000)
$ ldd prog
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe18950000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f8c50cb4000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f8c51077000)
$ ldd /bin/ls
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007fff41141000)
libselinux.so.1 => /lib64/libselinux.so.1 (0x00007f11d1688000)
libcap.so.2 => /lib64/libcap.so.2 (0x00007f11d1482000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f11d10bf000)
libpcre2-8.so.0 => /lib64/libpcre2-8.so.0 (0x00007f11d0e3b000)
libdl.so.2 => /lib64/libdl.so.2 (0x00007f11d0c37000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f11d1ad5000)
libpthread.so.0 => /lib64/libpthread.so.0 (0x00007f11d0a17000)
STATIC V.S DYNAMIC LIBRARIES
STATIC LIBRARIES CONS
- generate bigger executable files since library is integrated inside executable
- less memory efficient - each program has their own copy of the library
- Not easy to update - Requires all programs to update their copy of the library if a bug exists
Drawback of Dynamic Libraries
- Since many programs link to the same library, can cause compatibility issues if library gets updated or removed
- Extremely annoying to install programs

Interesting Example
expr evaluates expression (i.e. a calculator)$ expr 2 \* 2
4What happens if the library used by expr is corrupted?
$ expr 2 \* 2
8589934592A pseudo install of a program contained libgmp which caused an issue
$ ldd `which expr`
linux-vdso64.so.1 => (0x0003fff9d4800000)
libgmp.so.10 > /home/user/program/lib/libgmp.so.10 (0x00003fff9df00000)
libc.so.6 => /lib64/power8/libc.so.6 (0x00003fff9d200000)
/lib64/ld64.so.2 (0x00000000749a0000)